Explore a world where managing diabetes becomes effortless with the power of mobile and wearable tech! Dive into the realm of continuous glucose monitors, insulin pumps, smartwatches, and more. Uncover the secrets of seamless diabetes management, enhancing your well-being one device at a time!
Thank you for reading this post, don't forget to subscribe!How to Manage Diabetes with Mobile and Wearable Technology
Living with diabetes requires constantly monitoring blood sugar levels, diet, and physical activity. The advent of mobile and wearable technology has revolutionized the way individuals manage their diabetes. Continuous glucose monitors (CGMs), insulin pumps, smartwatches, fitness trackers, and blood sugar tracking apps have become integral to diabetes management, offering real-time insights and enhancing overall well-being.
With advancements in technology, managing diabetes has become more accessible and practical. Mobile and wearable technology significantly monitor diabetes-related parameters, offering individuals greater control over their health. In this blog post, we’ll explore how these devices positively impact the lives of people with diabetes.
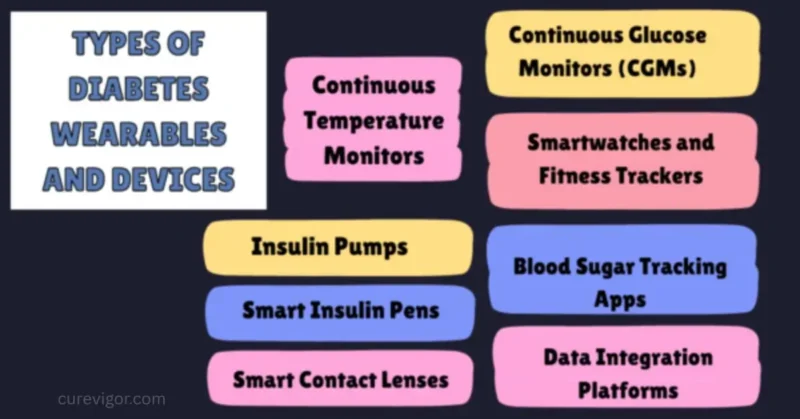
Types of Diabetes Wearables and Devices
Continuous Glucose Monitors (CGMs)
Continuous Glucose Monitors are wearable devices that provide real-time readings of blood sugar levels. These devices use a tiny sensor inserted under the skin to measure glucose levels throughout the day, offering continuous data to help individuals manage their diabetes more effectively.
Insulin Pumps
Insulin pumps are small, wearable devices that deliver a continuous supply of insulin throughout the day. They replace the need for multiple daily injections and can be programmed to provide additional insulin during meals. Some modern insulin pumps integrate with CGMs, creating a closed-loop system for automated insulin adjustments.
Smartwatches and Fitness Trackers
Smartwatches and fitness trackers have evolved to include health monitoring features relevant to diabetes management. These devices can track physical activity, monitor heart rate, and sometimes provide blood sugar readings. They serve as holistic health companions, offering insights into overall well-being.
Blood Sugar Tracking Apps
Mobile applications designed for blood sugar tracking are integral to diabetes management. These apps allow users to log glucose readings and track trends over time and often include features for meal logging, medication reminders, and data sharing with healthcare providers.
Smart Insulin Pens
Smart insulin pens are digital versions of traditional insulin pens. They allow users to track insulin doses digitally, providing insights into their insulin usage patterns. Some smart pens also offer features like dose reminders and data synchronization with mobile apps for a more comprehensive overview of diabetes management.
Continuous Temperature Monitors
These wearables monitor skin temperature continuously. Changes in skin temperature can sometimes indicate changes in blood flow, which may be relevant to diabetes management, particularly in preventing complications related to poor circulation.
Smart Contact Lenses
Under development, intelligent contact lenses aim to measure glucose levels in tears. These lenses could provide a non-invasive and continuous monitoring solution, offering a discreet and convenient way to track blood sugar levels.
Data Integration Platforms
Some devices act as data hubs, integrating information from various wearables and devices, including CGMs, insulin pumps, and fitness trackers. These platforms provide a comprehensive view of an individual’s health data, facilitating more informed decision-making in diabetes management.
These types of diabetes wearables and devices contribute to a more personalized and connected approach to diabetes care, offering individuals a range of options to monitor and manage their condition effectively. As technology continues to advance, the landscape of diabetes wearables is likely to expand, providing even more innovative solutions for individuals living with diabetes.
The introduction of smart insulin pens modernized traditional insulin pens. These pens deliver insulin doses and record the time and amount administered. The data is transferred to a mobile app, offering a comprehensive overview of insulin usage over time. Users and healthcare providers can adjust treatment plans accordingly.
Mobile Apps for Diabetes Management
In the era of digital health, mobile apps have emerged as invaluable tools for managing diabetes. These applications cater to the diverse needs of individuals with diabetes, offering features that streamline daily tasks, enhance monitoring capabilities, and promote overall well-being. Let’s explore the world of mobile apps designed to empower and support those navigating the complex landscape of diabetes management.
Blood Sugar Tracking Apps
At the core of diabetes management apps are those dedicated to blood sugar tracking. These apps allow users to log and monitor their glucose levels regularly. Features often include customizable input for meals, insulin doses, and physical activity, providing a comprehensive view of the factors influencing blood sugar fluctuations over time.
Medication Reminder Apps
Consistency is vital in managing diabetes medications. Medication reminder apps ensure that individuals never miss a dose. These apps offer timely notifications, helping users stay on track with their prescribed medication regimens.
Meal Planning and Nutrition Apps
Maintaining a balanced diet is crucial for diabetes management. Meal planning and nutrition apps assist users in making informed dietary choices. They may offer features like carbohydrate counting, food databases, and meal tracking to help individuals better understand and manage their nutritional intake.
Data-Sharing Apps
Effective communication with healthcare professionals is integral to diabetes care. Data-sharing apps enable users to share their blood sugar readings, medication adherence, and lifestyle habits with their healthcare team. It facilitates more informed and collaborative decision-making, even in virtual or remote healthcare settings.
Diabetes Community and Support Apps
Living with diabetes can be challenging, and a supportive community can make a significant difference. Some apps create a space for individuals to connect, share experiences, and seek advice from others facing similar challenges. These platforms foster a sense of community and provide emotional support, which is crucial in managing the emotional aspects of diabetes.
Fitness and Activity Tracking Apps
Physical activity plays a crucial role in diabetes management. Fitness and activity tracking apps go beyond step counting, offering features that monitor various types of physical activity. These apps help users set and achieve fitness goals, promoting a more active and health-conscious lifestyle.
Benefits and Impact of Wearables on Diabetes Management
Living with diabetes requires a vigilant and proactive approach to monitoring various health parameters. In recent years, wearable technology has emerged as a game-changer in diabetes management, offering a range of benefits that significantly impact the lives of individuals with this condition. Let’s explore wearables’ key advantages and transformative impact on diabetes management.
Real-Time Monitoring
One of the most significant benefits of wearables in diabetes management is their ability to provide real-time monitoring of crucial health metrics. For example, continuous Glucose Monitors (CGMs) offer constant and instant updates on blood sugar levels, allowing users to make informed decisions about their diet, insulin dosages, and overall lifestyle.
Improved Blood Sugar Control
Wearables enhance blood sugar control by providing a more comprehensive understanding of daily glucose trends. This real-time data empowers individuals to make timely adjustments to their insulin levels, reducing the risk of hyperglycemia or hypoglycemia and promoting better overall glycemic control.
Enhanced Treatment Personalization
The data generated by wearables facilitates a more personalized approach to diabetes treatment. Healthcare providers can analyze trends over time, tailor medication regimens, and offer targeted advice based on individual responses to different activities, meals, and stressors.
Integration of Devices
Wearable devices often integrate seamlessly with other technologies, creating a connected ecosystem. For example, CGMs can combine with insulin pumps, forming a closed-loop system that automates insulin delivery based on real-time glucose data. This integration streamlines diabetes management, reduces individual burden, and improves treatment accuracy.
Lifestyle Insights
Beyond glucose monitoring, wearables offer insights into various lifestyle factors. Smartwatches and fitness trackers provide data on physical activity, sleep patterns, and stress levels. Understanding these factors helps individuals make lifestyle adjustments that positively impact their overall health and contribute to better diabetes management.
Increased Patient Engagement
Wearables foster a sense of engagement and empowerment among individuals with diabetes. The ability to actively monitor and manage their health encourages a proactive approach to self-care. As a result, individuals become more involved in their treatment, leading to improved adherence to medications, dietary recommendations, and overall wellness practices.
Remote Monitoring and Telehealth
Wearable technology facilitates remote monitoring, allowing healthcare providers to access real-time data without frequent in-person visits. All that is particularly valuable for telehealth consultations is enabling timely adjustments to treatment plans and promoting regular communication between patients and healthcare professionals.
Quality of Life Enhancement
Ultimately, the impact of wearables on diabetes management translates into an enhanced quality of life. Reducing the daily burdens associated with traditional monitoring methods, coupled with the empowerment to take proactive control of one’s health, contributes to a more positive and fulfilling life for individuals managing diabetes.
Tailored Treatment Plans
Personalized diabetes care starts with creating treatment plans specifically designed to meet the unique needs of each individual. It involves a comprehensive look at a person’s health profile, including factors such as age, gender, medical history, comorbid conditions, and lifestyle habits. For example, younger patients might require different management strategies than older adults, and individuals with type 1 diabetes may have different needs than those with type 2.
In addition to standard medical factors, lifestyle elements such as diet, activity levels, and stress factors are also considered. By customizing treatment plans based on these variables, healthcare providers can create more effective, targeted strategies for managing diabetes and minimizing complications.
Precision Medication Adjustments
In personalized diabetes care, medication is tailored to an individual’s specific needs, and adjustments are made in real-time based on continuous data. Continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) and wearable devices provide up-to-date information about blood sugar levels daily and nightly, allowing healthcare providers to make precise adjustments to medication regimens.
For example, if a patient’s blood glucose levels are consistently high after meals, their insulin dosage may be modified accordingly. Treatment can be continuously fine-tuned using data from these monitoring devices to achieve the best possible blood sugar control. This precision approach not only helps in managing diabetes more effectively but also minimizes the risk of hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) or hyperglycemia (high blood sugar), making the treatment more individualized and responsive.
Customized Nutritional Guidance
Diet plays a critical role in diabetes management, and personalized care ensures that nutritional guidance is tailored to an individual’s health profile and preferences. For example, two people with diabetes may have different nutritional needs depending on their age, activity level, and cultural or dietary preferences. A customized nutritional plan could involve recommendations for macronutrient distribution (carbohydrates, fats, and proteins) based on an individual’s blood sugar patterns, weight management goals, and overall health objectives.
It can include advice on meal timing, portion control, and food choices that help maintain stable blood sugar levels throughout the day. For people with specific dietary needs (such as vegetarian, gluten-free, or ketogenic diets), personalized care can provide the necessary adjustments to ensure blood sugar control and overall nutritional balance.
Targeted Lifestyle Recommendations
Lifestyle factors—such as physical activity, sleep, and stress management—play an essential role in diabetes control. Personalized diabetes care recognizes that each individual’s lifestyle influences their blood sugar levels and overall well-being differently. Tailored recommendations may include creating an exercise plan suited to the person’s fitness level, preferences, and medical considerations (e.g., joint issues, cardiovascular health).
Similarly, stress management techniques such as mindfulness, meditation, or yoga might be recommended to help reduce stress, which can adversely affect blood glucose levels. Additionally, establishing healthy sleep patterns is crucial, as poor sleep can impact insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism. Targeted lifestyle recommendations ensure that diabetes management is integrated with a holistic approach, considering the broader factors influencing health beyond just medication.
Continuous Monitoring and Feedback
One of the cornerstones of personalized diabetes care is the ability to continuously monitor health metrics, such as blood glucose levels, activity, sleep, and even heart rate. Technologies like continuous glucose monitors (CGMs), fitness trackers, and mobile apps offer real-time insights that empower individuals to make informed decisions about their care.
This constant monitoring allows for ongoing adjustments to treatment plans, ensuring that interventions are always aligned with a person’s current health status. For example, if a person’s glucose levels fluctuate due to changes in their daily routine, immediate feedback from a monitoring system can prompt changes in medication or lifestyle practices.
This real-time, feedback-driven approach enables individuals to be more engaged in their care, improving outcomes and quality of life by maintaining better control over their diabetes and preventing complications.
Choosing the Right App
With the proliferation of health apps designed for diabetes management, choosing the one that best fits an individual’s needs can be challenging. When selecting an app, it is essential to consider several factors that align with personal preferences and health requirements. Some people may prioritize ease of use, while others may need advanced features like integration with continuous glucose monitors (CGMs), insulin pumps, or other wearable devices.
Features such as meal tracking, medication reminders, activity logs, and educational content may also be essential to consider. Additionally, apps that provide data-sharing capabilities with healthcare providers or offer coaching and support may be particularly valuable for individuals who need more guidance.
Choosing the right diabetes management app involves understanding one’s goals—tracking daily blood sugar levels, managing insulin doses, or simply staying motivated to follow a treatment plan—and selecting an app that offers the best functionality, convenience, and personalization.
Each of these components reflects the shift towards more personalized, data-driven diabetes care, where treatment, nutrition, and lifestyle factors are adjusted to meet the individual’s unique needs. By using technology and tailoring approaches to each person, diabetes management becomes more proactive and precise, ultimately leading to better outcomes.
FAQs
Q: What are the mobile apps for diabetes?
Numerous mobile apps cater to various aspects of diabetes management. Some popular ones include:
- MySugr is a comprehensive blood sugar tracking, meal logging, and insulin dose management app.
- Blood Sugar Tracker: Allows users to log glucose readings, track trends, and manage medications.
- Diabetes: M offers features for tracking blood sugar, drugs, and physical activity.
Q: What is the app for diabetes self-management?
For diabetes self-management, consider apps that provide a holistic approach, covering aspects like blood sugar tracking, medication reminders, meal planning, and lifestyle monitoring. Apps like “MySugr” and “Diabetes: M” are designed to empower individuals to manage their diabetes independently.
Q: What is the best app for preventing diabetes?
While no app can guarantee diabetes prevention, several apps focus on promoting a healthy lifestyle, which can contribute to diabetes prevention. Apps like “MyFitnessPal” and “Lark” offer features for tracking nutrition, exercise, and weight management (supporting overall health and reducing the risk factors associated with diabetes).
Q: What is the mobile phone technology for diabetes?
Mobile phone technology for diabetes encompasses a range of applications and features designed to assist individuals in managing their conditions. It includes:
- Blood Sugar Tracking Apps: Users can monitor and log glucose levels regularly.
- Medication Reminder Apps: Ensure consistent adherence to prescribed medication regimens.
- Meal Planning and Nutrition Apps: Assist in making informed dietary choices.
- Data Sharing Apps: Facilitate communication with healthcare professionals.
- Diabetes Community and Support Apps: Provide a space for individuals to connect and share experiences.
Q. What is wearable technology for diabetes management?
Wearable technology for diabetes management refers to devices that individuals can wear to monitor and control aspects of their diabetes. These include continuous glucose monitors (CGMs), insulin pumps, smartwatches, and fitness trackers designed to track vital parameters, providing real-time data to enhance diabetes care.
Q. What is the mobile phone technology for diabetes?
Diabetes-related mobile phone technology includes various features and applications that help people manage their condition. These technologies aim to make diabetes management more accessible and convenient through mobile devices.
Q. What technology is used to manage diabetes?
Several technologies are used to manage diabetes effectively. Continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) provide real-time blood sugar readings; insulin pumps deliver precise insulin doses; smartwatches and fitness trackers monitor overall health. Mobile apps assist in tracking blood sugar levels, meals, and medications. The integration of these technologies offers a comprehensive approach to diabetes management.
Q. What are the mobile apps for diabetes?
Mobile apps for diabetes cover a range of functionalities. Some apps focus on blood sugar tracking, allowing users to log and monitor glucose levels. Others include medication reminders, meal tracking, and data-sharing features for better communication with healthcare providers. Popular diabetes management apps include MySugr, Blood Sugar Tracker, and MyFitnessPal.
Q. What is wearable technology for type 1 diabetes?
Wearable technology for type 1 diabetes includes devices like continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) and insulin pumps. CGMs provide real-time blood sugar data, while insulin pumps offer a convenient and precise delivery method. These devices help individuals with type 1 diabetes manage their condition more effectively, reducing the need for frequent injections and offering better control over blood sugar levels.
Q. What are the six digital health technologies that will transform diabetes?
The six digital health technologies that will transform diabetes include:
- Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM): Provides real-time blood sugar data.
- Artificial Pancreas Systems: Integrates CGMs and insulin pumps to automate insulin delivery.CGMs and insulin pumps are integrated with artificial pancreas systems to automate insulin delivery.
- Smart Insulin Pens: Digitally track insulin doses and offer reminders.
- Platforms for telemedicine: Enable online consultations with medical specialists.
- Mobile Health Apps: Assist in blood sugar tracking, meal planning, and medication management.
- Wearable Health Tech: Includes smartwatches and fitness trackers that monitor overall health and activity levels.
Conclusion
Mobile and wearable technology have ushered in a new era in diabetes management. Continuous glucose monitors (CGMs), insulin pumps, smartwatches, fitness trackers, and blood sugar-tracking apps empower individuals with diabetes to take control of their health.
These devices provide real-time data, streamline daily routines, and contribute to an improved quality of life. While challenges and questions may arise, the ongoing advancements in wearable technology for diabetes promise a brighter future for those living with this condition. Embracing these innovations opens doors to more personalized and effective diabetes care.
Mobile apps have transformed the landscape of diabetes management, putting control and information directly in the hands of individuals. From real-time blood sugar tracking to fostering a sense of community, these apps are pivotal in empowering diabetes patients. As technology advances, the future holds even more promise for innovative solutions that simplify and enhance the journey of diabetes management, contributing to better health outcomes and an improved quality of life.
Read more articles on Health and Wellness.
You may like to read:
Ultimate Guide to Hair Loss Prevention: Top Products and Proven Solutions

