Don’t fall for the hype. Before you try African mango seed extract for weight loss, read this. We cover common side effects, potential drug interactions, and crucial safety information you need to know to protect your health.
Thank you for reading this post, don't forget to subscribe!While African mango is popular, it’s a supplement that requires an innovative, informed approach. Irvingia gabonensis seeds are used to make African mango seed extract, which has gained popularity as a natural weight loss aid.
Promoted for its ability to suppress appetite, boost metabolism, and regulate cholesterol and blood sugar levels, it’s easy to see why consumers are turning to this tropical remedy. However people are getting benefits by using African mango seed extract.
First of all, always go to your doctor, your healthcare provider, or your physician.

However, despite the growing popularity, there are serious concerns you must not ignore. In this article, we uncover the potential side effects, interactions, and precautions that could help you make an informed decision.
What Is African Mango Seed Extract?
African mango seed extract comes from a fruit native to West and Central Africa. Its extract has recently been advertised as a supplement, mainly for weight loss, but it has long been taken for its nutritional and therapeutic benefits.
Essential active ingredients consist of:
- Soluble fiber: Supports digestive health and fullness.
- Agents that modulate leptin may have an impact on hunger and fat metabolism.
- Antioxidants: Prevent inflammation and combat free radicals.
Many users report benefits such as reduced body fat, improved cholesterol levels, and lower blood glucose. But these results are often based on short-term studies and don’t fully explore the risks. But talk to your doctor first when you think of starting to take it.
Common Side Effects of African Mango Seed Extract
Although it is frequently promoted as a natural and generally safe weight loss supplement, African mango seed extract (Irvingia gabonensis) has several disadvantages. Users often report several mild to moderate side effects, especially during the early stages of supplementation.
Depending on the person’s health, dosage, and sensitivity to plant-based chemicals or dietary fiber, these reactions can range in intensity. Consequently, seeking advice from a healthcare expert is essential.
Gastrointestinal Distress: A Common First Reaction
African mango is rich in soluble fiber—a component that supports digestive health but can overwhelm the gastrointestinal (GI) system when introduced too rapidly.
Bloating
Many users feel a sense of abdominal fullness or swelling shortly after starting supplementation. It occurs due to increased fermentation of fiber in the gut, which produces gas and pressure.
Gas and Flatulence
Excess gas is one of the most reported side effects. As beneficial gut bacteria break down the unfamiliar fiber, gas is released as a byproduct, leading to discomfort or social embarrassment.
Diarrhea
High fiber intake can accelerate bowel movements. For some, this results in loose stools or frequent urges to use the restroom, especially when the body hasn’t yet adjusted.
Constipation
In contrast, others may experience the opposite effect. Without adequate water intake, the fiber can slow digestion and harden stools, resulting in difficulty passing waste.
Tip: To reduce GI symptoms, doctors recommend starting with a low dose and increasing gradually while ensuring proper hydration. However, talk to your doctor first when you start taking such a dose.
Headaches and Dizziness: Blood Sugar Fluctuations
The glycemic regulation of the body may be affected by African mango. It can lower blood sugar levels by increasing insulin sensitivity and reducing appetite, sometimes to an extreme degree. The precious words are these: consult your doctor or healthcare provider first.
Lightheadedness
Sudden drops in blood glucose can lead to feeling faint, especially if the supplement is taken on an empty stomach or alongside blood sugar-lowering medication.
Nausea
A general sense of queasiness may accompany changes in metabolism, especially when paired with other supplements or if used in high doses.
Headaches
Tension or throbbing headaches may arise due to blood sugar imbalances or mild dehydration linked to the supplement’s diuretic-like effect.
Caution: Before consuming African mango, people with diabetes or hypoglycemia should speak with their doctor because it may interact with insulin or oral diabetic medicines.

Sleep Disturbances: Stimulatory Side Effects
Though not a stimulant in the traditional sense, African mango can subtly activate the nervous system by increasing metabolic rate and energy utilization.
Restlessness
Some users feel more alert or jittery, particularly in the evening, which can interfere with winding down for sleep.
Difficulty Falling Asleep
Increased metabolic activity can cause sleep-onset insomnia by interfering with the body’s normal circadian rhythm or delaying the generation of melatonin.
Strange or Vivid Dreams
Anecdotal reports describe unusually intense or bizarre dreams. It could be a neurological side effect of altered neurotransmitter levels or deeper REM sleep patterns caused by metabolic changes.
Advice: Taking the supplement earlier in the day may help minimize nighttime disturbances. But remember to consult a doctor first.
Rare but Serious: Allergic Reactions
Though uncommon, allergic reactions to African mango can occur, especially in individuals with sensitivities to mangoes or tree nuts.
Hives and Skin Irritation
Symptoms such as hives, redness, or itchiness have been reported following supplement intake. These responses may happen in a matter of minutes or hours.
Itchy Skin and Rashes
Mild dermatitis-like symptoms may persist for several days. These can worsen with continued use if not adequately addressed.
Swelling of the Face or Throat
In rare but severe cases, users have experienced angioedema—swelling that affects the lips, eyes, tongue, or throat. This could indicate a life-threatening allergic reaction requiring emergency care.
Important: If you have a known mango, latex, or nut allergy, avoid African mango supplements unless cleared by a physician. Always read ingredient labels to ensure there are no cross-reactive substances.
These side effects, while not experienced by all, highlight the importance of cautious and informed use. Starting with the smallest adequate amount is always advised, along with staying hydrated, regularly monitoring your body’s reaction, and seeking medical advice if you are taking medication or are treating a chronic disease.
The key to safe supplementation lies in awareness and personalization.
Serious Risks and Long-Term Side Effects
Irvingia gabonensis is frequently marketed as a “safe” and “natural” weight-loss solution; however, “natural” does not always imply innocuous. The marketing is supported by an increasing amount of anecdotal evidence and clinical concerns that call for prudence, particularly for long-term users or those with underlying medical issues.
Below, we explore some of the most concerning long-term and serious side effects of African mango seed extract.
Liver Toxicity: An Emerging Concern
The liver is essential for breaking down the chemicals we consume, including dietary supplements. Although there is no concrete evidence linking African mango to liver failure, a few case studies and isolated reports point to a potential link with inflammation and hepatic stress. The assistance of a specialist, such as a doctor, is crucial.
What We Know:
- After using African mango extract for a long time, some consumers reported having raised liver enzymes, which is indicative of liver strain.
- A handful of case reports have noted drug-induced hepatitis potentially linked to unregulated or contaminated supplement batches.
- Fatigue, nausea, pain in the upper right abdomen, and jaundice (yellowing of the skin or eyes) are possible symptoms.
Takeaway: Anyone with existing liver conditions—such as hepatitis, cirrhosis, or fatty liver disease—should avoid this supplement unless advised by a healthcare provider. Periodic liver function tests may be necessary if using African mango long-term.
Hormonal Interference: Metabolic and Reproductive Impacts
African mango extract may affect hormones that control metabolism and appetite. While this is part of its intended mechanism for promoting weight loss, it also raises concerns about hormonal dysregulation, especially when taken in large or extended doses. These are all information and tips, but you must consult a doctor first.
Affected Hormones:
- Leptin: African mango may increase leptin sensitivity, which could suppress appetite but also interfere with normal hormonal balance, particularly in women of reproductive age.
- Insulin: By enhancing insulin sensitivity, it may lower blood sugar unpredictably, posing a risk to those with diabetes or hypoglycemia.
- Adiponectin: This hormone plays a role in fat metabolism and inflammation; alterations could have unintended consequences on energy regulation and immune response.
Potential Risks:
- Irregular menstrual cycles
- Fertility issues (due to hormonal shifts)
- Mood disturbances are linked to blood sugar imbalances.
- Increased fatigue or adrenal strain in long-term users
Note: Individuals with endocrine disorders (like PCOS, thyroid disease, or adrenal insufficiency) should use extreme caution and consult an endocrinologist before using this supplement.
Blood Pressure and Heart Rate Fluctuations
While not a stimulant in the traditional sense, African mango extract may influence cardiovascular function through metabolic stimulation and hormonal activity.
Reported Cardiovascular Effects:
- Heart Palpitations: Users describe irregular or racing heartbeats after starting supplementation.
- Tachycardia (elevated heart rate): In some cases, resting heart rates exceed 100 bpm, particularly when taken with caffeine or other weight loss supplements.
- Hypotension (low blood pressure): For individuals on blood pressure medications, African mango may further lower BP, leading to dizziness, fainting, or blurred vision.
These side effects pose serious risks to those with pre-existing heart conditions, such as arrhythmia, hypertension, or congestive heart failure.
Caution: People on cardiovascular medications or with a history of heart disease should avoid African mango unless under strict medical supervision.
Drug Interactions: A Hidden but Serious Risk
African mango may appear harmless at first glance, but its active compounds can interact with common prescription medications, sometimes with dangerous consequences. These interactions could change how the body absorbs, metabolizes, or eliminates medications.
Known Interactions Include:
- Diabetes Medications (e.g., insulin, metformin, glipizide):
- African mango’s blood sugar-lowering properties may potentiate hypoglycemia, leading to shakiness, confusion, or loss of consciousness.
- Blood Thinners (e.g., warfarin, aspirin, clopidogrel):
- The extract may have a mild anticoagulant effect, increasing the risk of internal bleeding, especially in those taking anticoagulants or undergoing surgery.
- Blood Pressure Medications (e.g., beta-blockers, ACE inhibitors):
- Combined use could lead to dangerously low blood pressure (hypotension), causing dizziness, fatigue, or syncope (fainting).
- Antidepressants and MAO Inhibitors:
- Though data is limited, some users have reported neurological symptoms, such as agitation, confusion, or sleep disturbances. The supplement may affect neurotransmitter regulation indirectly.
Reminder: Always inform your healthcare provider of any supplements you are taking. Natural products can still interfere with prescription medications and change their effectiveness or safety profile.
African mango seed extract may offer weight management support for some users, but the potential for serious health risks cannot be ignored. Liver toxicity, hormonal imbalances, cardiovascular strain, and dangerous drug interactions are all valid concerns — particularly for those using the supplement long-term or in high doses.
To use it responsibly:
- Limit intake to clinically recommended dosages
- Avoid combining with other stimulants or medications without professional advice
- Monitor your body’s signals, especially if you feel “off” or unwell after use
- Consider safer, better-studied alternatives if you have underlying health conditions
Who Should Avoid African Mango Seed Extract?
African mango is not suitable for everyone. The following groups should avoid it or use it only under medical supervision:
- Pregnant or breastfeeding women: No safety studies available
- People with diabetes: Increased risk of hypoglycemia
- Individuals on blood thinners or heart medications: Risk of adverse interactions
- People with liver disease or hormone-sensitive conditions
- Children under 18: Not studied for pediatric use
- Allergy-prone individuals: Especially those allergic to nuts or mangoes
The Problem With Supplement Quality and Regulation
The dietary supplement industry is poorly regulated in many countries. Prioritize quality over price. This tip is particularly relevant and helpful because the supplement sector isn’t as strictly controlled as pharmaceuticals.
Lack of FDA Oversight
Unlike prescription medications, dietary supplements do not receive prior approval from the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) before entering the market:
- Ingredients may not match the label
- Contaminants or banned substances may be present
- Dosages can be inconsistent
Purity and Potency Concerns
Supplements are not all made equal. To ensure that you’re getting a safe and pure product, look for businesses that have completed third-party testing by organizations like the USP (U.S. Pharmacopeia) or NSF International.
These seals attest to the product’s potency, quality, and purity as well as the absence of any dangerous or concealed substances.
The Wild Card Factor
Because there’s no standardization, every brand may offer a vastly different product. What worked for one person might harm another.
Supplement Risk Flow
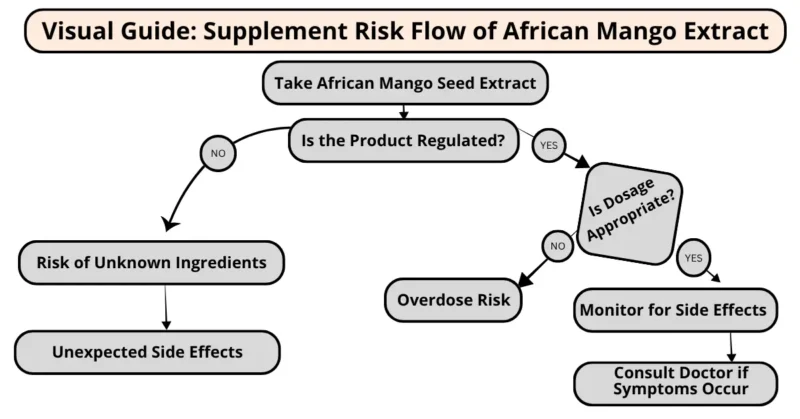
Safe Use Guidelines for African Mango Seed Extract
See a physician, pharmacist, or qualified nutritionist before beginning any new supplement regimen, including African mango seed extract. They can provide personalized advice based on your health history, current medications, and individual needs, helping you avoid potential risks and interactions.
If you choose to try African mango, do so cautiously.
Recommended Dosage
Stick to research-supported dosages, typically:
- 150 mg to 1,050 mg per day, divided into 2-3 doses
- Always start with the lowest effective dose.
Choose Trusted Brands
Look for:
- Third-party lab testing (e.g., USP, NSF)
- Clear labeling of dosage and ingredients
- Transparent sourcing and manufacturing practices
Monitor Your Body
Watch for:
- Skin reactions
- Gastrointestinal changes
- Heart palpitations
- Mood swings or dizziness
Discontinue immediately if any symptoms appear.
Safer Natural Alternatives for Weight Loss
A healthy lifestyle is not something that supplements can replace.
Keep in mind that supplements are meant to complement a good diet and active lifestyle, not to replace them. A healthy diet, consistent exercise, enough sleep, and stress reduction are the foundations of true, long-lasting wellness.
The African mango, even at its best, is just one part of a much larger whole. Look at alternatives with fewer known side effects:
| Supplement | Benefits | Risks |
|---|---|---|
| Green Tea Extract | Boosts metabolism, antioxidant-rich | May cause jitteriness |
| Glucomannan | Promotes fullness, lowers cholesterol | Can cause gas and bloating |
| Garcinia Cambogia | May suppress appetite | Mixed evidence, potential liver effects |
| Apple Cider Vinegar | May curb appetite | Acidic, can damage teeth |
FAQs
Q. What is African mango seed extract used for?
The main application for African Mango Seed Extract is as a natural weight-loss aid. It’s derived from the seeds of Irvingia gabonensis, a fruit native to West Africa—soluble fiber, which is abundant in the extract, aids in reducing hunger and promoting fullness. Many users also take it to support blood sugar control and cholesterol management.
Some believe it improves metabolic function by influencing hormones like leptin. While marketed as a fat-burning solution, scientific evidence is still evolving.Before using African mango extract for medical purposes, it is recommended to speak with your doctor.
Q. Are there any side effects of African mango extract?
Indeed, some consumers may have mild to moderate adverse effects from African mango extract. Bloating, gas, diarrhea, and headaches are common problems, particularly during the first few days. Because blood sugar levels fluctuate, it may also interfere with sleep or make you feel lightheaded.
In rare cases, allergic reactions can include stinging or swelling. It may occasionally interact with pharmaceuticals like blood thinners or diabetes treatments. Long-term use of African mango seed supplements has raised concerns about liver and hormonal health. Always begin with a small dosage and keep an eye on how your body reacts.
Q. Is African mango seed extract safe for people with diabetes?
Although African mango seed extract may help control blood sugar, people with diabetes should use caution. When used with diabetic drugs, the extract may increase insulin sensitivity and result in hypoglycemia. Following use, some users have complained of weariness, shakiness, or dizziness.
When beginning the supplement, it is imperative to keep a constant eye on glucose levels. Consulting your healthcare provider is highly recommended before taking African mango extract. Every diabetic’s medication plan is unique, and interactions can be serious. Natural doesn’t always mean safe, especially when chronic conditions are involved.
Q. Can African mango extract help with weight loss?
African mango extract is widely marketed for its weight-loss benefits, thanks to its appetite-suppressing and metabolism-boosting properties. In addition to slowing digestion, it makes you feel fuller for longer. Some studies show modest fat and weight reduction when combined with diet and exercise.
However, results vary, and it’s not a miracle pill. The extract may influence hormones like leptin and adiponectin, which are involved in fat storage and metabolism. Sustainable weight loss still depends on healthy lifestyle choices. African Mango Seed Extract could complement those initiatives rather than take their place.
Q. Who should avoid taking African Mango Seed Extract?
Specific individuals should avoid African Mango Seed Extract due to potential risks and interactions. Pregnant or breastfeeding women should not use it, as safety data is lacking. People with liver problems, hormonal disorders, or cardiovascular conditions may be at risk of complications.
Those on blood pressure meds, blood thinners, or diabetes medication should use extreme caution. Children and individuals with mango or nut allergies should also avoid it. African Mango Extract, although natural, can cause serious issues if misused. Always get medical advice before incorporating any supplements into your regimen.
The Bottom Line
Be Informed, Not Influenced
In the end, African mango seed extract is not a magic bullet for weight loss. While its natural origins might sound appealing, the reality is that it’s a powerful supplement with potential side effects and a lack of comprehensive, long-term research. The key takeaway is to approach this supplement with a healthy dose of skepticism and caution.
Before you start taking African mango, or any new supplement, the single most important step is to have an open and honest conversation with your doctor.They can help you weigh the potential benefits against the risks, especially if you have pre-existing health conditions or are taking other medications. Remember, your well-being is more valuable than any quick fix.
The excitement surrounding African mango seed extract is real—but so are the risks. What promises weight loss may bring unintended consequences if not used carefully.
Before adding it to your health routine:
- Talk to your doctor first, especially if you’re on medication or have a chronic condition.
- Start low and go slow.
- If you have negative side effects, pay attention to your body and stop.
If you want to take African mango, begin with the smallest dosage advised and closely monitor your body’s reaction. If you encounter any of the above side effects or other odd symptoms, stop taking the supplement right away and get in touch with your doctor.
Buyer beware—your health depends on what you put into your body. Choose wisely, and always prioritize safety over quick results.
Read more Wellness Tips.
You might like:

